Ceph OSD scaling and rebalancing
| 🌐 This document is available in both English and Ukrainian. Use the language toggle in the top right corner to switch between versions. |
This guide covers how to scale a Ceph cluster by adding new OSDs (Object Storage Daemons) and optimize the rebalancing process to prevent performance degradation.
|
Set up a Grafana alert to trigger when disk usage exceeds 75%. This gives you time to scale the cluster before storage runs out. |
1. Scaling OSDs
When your Ceph cluster is running low on storage, add new PVCs and increase the number of OSDs by updating the StorageCluster CR resource.
1.1. Adding OSDs via StorageCluster CR
-
Edit the
StorageClusterresource in theopenshift-storagenamespace:oc edit StorageCluster -n openshift-storage ocs-storagecluster -
Locate the
storage.storageClassDeviceSetssection and increase thecountvalue to add more OSD groups. Ensure the number ofreplicaandstoragesize per OSD group matches your requirements.
storage:
storageClassDeviceSets:
- name: ocs-deviceset-gp3-csi
count: 2 # was 1 — add one more group (1)
replica: 3 (2)
resources:
limits:
cpu: "4"
memory: 16Gi
requests:
cpu: "2"
memory: 8Gi
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: data
spec:
resources:
requests:
storage: 512Gi (3)
storageClassName: gp3-csi
volumeMode: Block
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce| 1 | count — number of OSD groups to deploy. Increasing by 1 adds a new group based on the given replica count. |
| 2 | replica — number of OSDs in each group. For example, replica: 3 deploys three OSDs per group. |
| 3 | storage — PVC size for each OSD. Here, each replica is allocated 512Gi. |
|
Before scaling, check the Capacity of existing PVCs. New OSDs must match the existing size to avoid imbalance. |
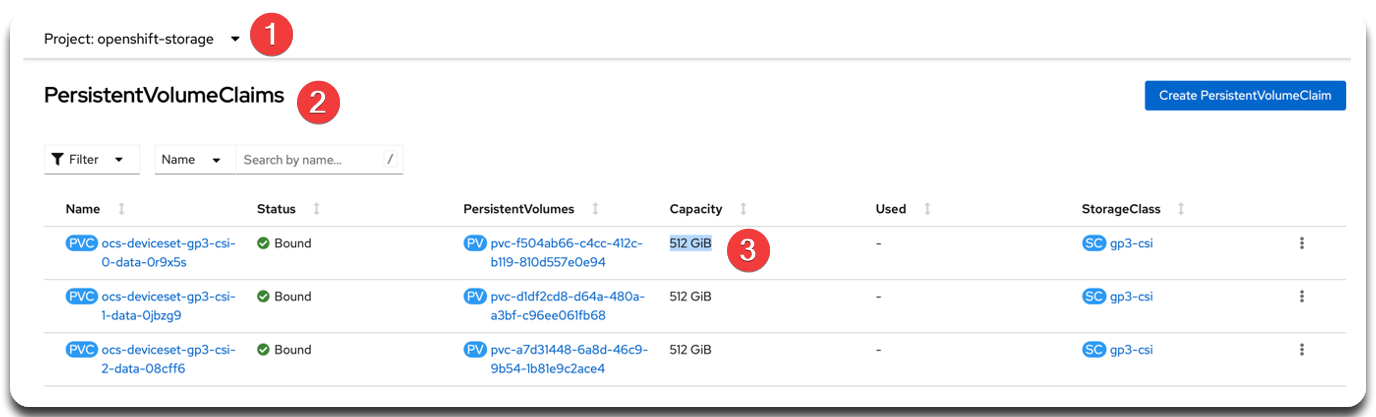
1.2. Verifying the result
Run the following commands to verify that the cluster has scaled:
-
Check Ceph cluster status:
ceph -s --conf=/var/lib/rook/openshift-storage/openshift-storage.configThis command shows the overall cluster state, including OSD count, monitor health, PG states, and replication status.
-
Check the OSD tree to confirm new OSDs were added:
ceph osd tree --conf=/var/lib/rook/openshift-storage/openshift-storage.configThis command displays the cluster OSD hierarchy, including host associations and status.
2. Configuring and optimizing rebalancing
After adding or removing OSDs, Ceph automatically triggers rebalancing — redistributing objects across OSDs to maintain balanced storage usage.
This process can be resource-intensive and may affect cluster performance. Use the parameters below to either throttle or accelerate the process, depending on your needs.
2.1. Throttling rebalancing
Use this option when maintaining stable performance during business hours is the priority.
-
Limit the number of parallel backfill threads:
ceph config set osd osd_max_backfills 1 --conf=/var/lib/rook/openshift-storage/openshift-storage.config ceph config set osd osd_recovery_max_active 1 --conf=/var/lib/rook/openshift-storage/openshift-storage.configThese settings reduce concurrent
backfillandrecoveryoperations to minimize impact on disk and CPU. -
Add delay between
recoveryactions:ceph config set osd osd_recovery_sleep 0.1 --conf=/var/lib/rook/openshift-storage/openshift-storage.configThis introduces a
0.1sdelay betweenrecoveryactions to reduce a disk and CPU load.
2.2. Speeding up rebalancing (Recommended during maintenance windows)
During low-traffic periods (e.g., overnight or weekends), you can speed up rebalancing by allowing more parallel operations:
ceph config set osd osd_max_backfills 4 --conf=/var/lib/rook/openshift-storage/openshift-storage.config
ceph config set osd osd_recovery_max_active 4 --conf=/var/lib/rook/openshift-storage/openshift-storage.configThese settings increase the number of simultaneous backfill and recovery operations. Use only during scheduled maintenance windows.
2.3. Monitoring Rebalancing Progress
Use these commands to monitor rebalancing activity and Placement Group status:
ceph -s --conf=/var/lib/rook/openshift-storage/openshift-storage.configDisplays current cluster status, including recovery, backfill, and degraded PGs.
ceph pg stat --conf=/var/lib/rook/openshift-storage/openshift-storage.configShows detailed PG statistics and their current state (active, clean, backfilling, recovering).
|
If the cluster remains in a |